This article has been reprinted with permission from the Dallas Morning News. It is the third installment in a series of essays by architecture critic Mark Lamster that tells the history of Dallas through the buildings that define the city. They will be collected in a volume to be produced by the nonprofit publishing house . Read earlier installments on and the .
How Dallas Became the World’s Capital of the Mall
Author
Mark Lamster
Affiliation
Dallas Morning News
Tags
With high design and high art, NorthPark Center made shopping glamorous for everyone.
As a child born and raised in New York City, I grew up with a distaste for malls. No, that’s not quite right. I hated them. Malls were for suburban kids, whom I disdained as uncultured rubes. They were the antithesis of the city life that I loved. Malls were car-dependent, boring, ugly, hermetically sealed bastions of conformity and mindless consumerism. The idea that anything quirky or different, anything of genuine originality might exist in or emerge from a mall seemed, to my adolescent brain, preposterous. I maintained this view well into adulthood.
Then I moved to Dallas.
Although there are cities with more malls (Jakarta has the most) and cities with larger malls (Tehran has the biggest), Dallas can rightly call itself the world’s capital of the mall. It’s easy to understand why. As a typology, the mall is ideally suited to Dallas, because the mall caters to two of the city’s favorite pastimes: driving and shopping. The mall didn’t quite originate in Dallas, but the city has played a significant role in its evolution. And it is in Dallas that the mall has reached its ideal form, its white-brick apotheosis. The place where it has done so is NorthPark Center, the mall to end all malls.
The story of the mall in Dallas does not begin with NorthPark, however, but a short distance away, off Hillcrest Boulevard. In 1926, the developer C.W. Snider announced plans for a self-contained, 30-acre shopping district there in University Park, then only two years old, its growth propelled by the emergence of the automobile as a primary means of everyday commuting. The principal innovation of was how it accommodated the motor vehicle: “parking streets” put angled spaces facing both shop fronts on one side and landscaped medians on the other.
A pastiche of a pastiche
The idea of a private shopping center as a de facto town center was extended at Highland Park Village, developed just a few years later by the brothers-in-law Hugh Prather and Edgar Flippen. Snider Plaza was just one of their models. Another was Kansas City’s Country Club Plaza, which opened in 1923. A fantasy Main Street outside of downtown in an appealing Spanish style, it set the design standard for suburban shopping centers. Its developer, J.C. Nichols, was a friend and adviser of Prather. There was another critical Dallas connection in its design team: Its layout was the work of George Kessler, who gave Dallas its urban plan after the catastrophic flood of 1908.
You might say that the architecture of Highland Park Village is a pastiche of a pastiche. To find inspiration for its design, Prather traveled to Spain with his architect, James Cheek, of the Dallas firm Fooshee & Cheek. They visited Granada and Seville, and then traveled to Barcelona for the International Exposition. While Mies van der Rohe’s was drawing attention as a luxurious exemplar of the new modernity, Prather and Cheek found their model in El Poble Espanyol, a mock Spanish village that plucked notable historic buildings from across the country and placed copies around a plaza with a bell tower.
Cheek took that architectural paradigm and adapted it into something suitable for an affluent American suburb, with a charming ensemble of buildings marked by red terra-cotta roofs, cast-stone decorative panels, wrought-iron lighting fixtures and redwood balconies. He also introduced the car, fusing the pedestrian scale he and Prather found in Spain with the “parking street” innovation of Snider Plaza. The initial design called for some 75 storefronts, a theater and parking for 470 cars.
But the timing could not have been worse. With the onset of the Depression, Prather and Flippen had trouble financing their shopping village, and when it did open in 1931, it was only partially occupied. But as the economy recovered, those slots filled in, eventually creating a town center that could fill every need: There was a gas station, a drug store, the upscale Hunt’s grocery, an A&P supermarket, a bank, restaurants and a post office. The most important of these early stores was an outlet of Volk Brothers department store that sold children’s shoes. It was the first chain department store to open outside of the downtown core, a Pied Piper of the retail migration to the suburbs.
Snider Plaza and Highland Park Village established that a shopping center outside of downtown could be a desirable destination and viable business proposition. But it was several decades before the mall transformed into what we know of the form today: an enclosed pedestrian environment floating in a sea of parking with highway access. That development was abetted by government policy. Federally funded highways encouraged suburban building along urban peripheries, and government-backed mortgages made the single-family house an attainable dream for American families. Of course, the benefits of that spending were not equally accessible to all Americans.
A total urban complex
If any single individual was responsible for the transformation of the mall in the postwar years, it was , an Austrian architect who, fleeing the Nazis, emigrated to the United States in 1938. Gruen quite literally wrote the book on the mall: , published in 1960, would serve as an essential guide for architects and developers. Gruen’s vision was to bring idealized downtowns to America’s rapidly developing suburbs, with shops on attractive pedestrian streets with landscaped plazas. He first demonstrated those principals in 1954 with the Northland Center, in the Detroit suburb of Southfield. It was followed two years later by Southdale Center, in the Minneapolis suburb of Edina. The latter was the first mall to be entirely enclosed, a response to the frigid Minnesota climate.
In Dallas, the climate challenge was not cold but heat, a problem that was no longer insoluble, thanks to technological advances in the field of air conditioning. Raymond Nasher understood that possibility. He was neither a planner nor a retailer, but he could surely recognize a good business opportunity. A native of Boston, he had attended the elite Boston Latin School before going on to Duke as an undergraduate and Boston University for a master’s degree in economics. He came to Dallas in 1950, the hometown of his wife, the former Patsy Rabinowitz, who would become his partner in the development of NorthPark. A woman of prodigious intelligence, she had graduated Highland Park High School at age 14, moving on to The Hockaday School, Southern Methodist University and Smith College. She met Nasher in Boston, at an election night party in 1948.
When the young couple arrived in Dallas, the city was in rapid postwar expansion, making it an ideal base of operations for an ambitious real estate developer, and Nasher was certainly that. By 1961, when his plans for a major shopping center at the intersection of Northwest Highway and the Central Expressway were made public, he was also at work on a luxury residential tower in Tulsa, an office complex in Beaumont, and a new city, West Hollywood, in South Florida. NorthPark would be the equivalent of a new downtown. “It will be a total urban complex rather than a shopping center,” he told The Dallas Morning News. “It’s like building the entire central business district of a large city.”
The site of that future development was still open pasture, but clearly in the path of the city’s growth. In the hopes of maximizing its return, the Hillcrest Foundation, which owned the property, had been reluctant to sell, delaying its transformation. Nasher convinced them to allow for development by agreeing to lease the property for 99 years, a deal that would net the foundation $50 million, a far higher return than it would have received from residential development.
The arrangement was not welcomed by some of NorthPark’s future neighbors, a contingent of whom was not keen on the idea of a 93-acre shopping center with 7,000 parking spaces. The Preston Hollow Home Owners Association fought the required zoning change for the property, the chief complaint being the prospect of increased traffic. “That area is already highly congested,” the group’s president told The News in 1961. This was NIMBYism avant la lettre, but the effort failed. The city, always pro-business and mindful of the philanthropic potential of a capitalized Hillcrest Foundation, approved Nasher’s development plan.
Like-minded partners
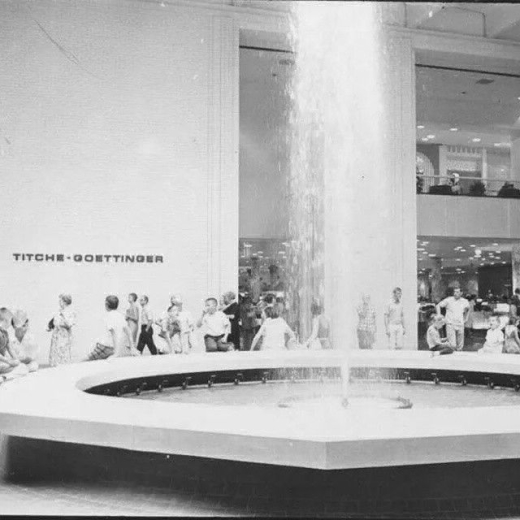
The next task: filling the mall with retailers that would attract shoppers. Nasher secured JCPenney and Titche-Goettinger as two of three anchor tenants. But the store he most prized was Neiman Marcus, a Dallas institution and national standard-bearer of luxury retail. Neiman’s presence would confer a level of glamour on NorthPark that would set it apart from other malls, making it a destination not just of convenience but aspiration.
In , the iconic store’s president, Nasher found a like-minded partner with a similar background, both being assimilated and highly educated Jewish men whose families had emigrated from Eastern Europe, where they had worked in the rag trade. The Nashers and Marcuses had become friends soon after the Nashers had arrived in Dallas. Patsy, in her school days, sold shoes at Neiman’s downtown flagship. Both the Nashers and the Marcuses were deeply entrenched in civic life, supporting the Dallas Symphony Orchestra, the Dallas Museum of Art and Temple Emanu-El.
Marcus, however, was initially reluctant to sign his department store up for Nasher’s development. He already had an outpost in Preston Center, and worried that NorthPark’s location was too far from his well-heeled Park Cities clients. But with the lease on that Preston Center location expiring, Marcus relented, although he insisted on his own architect, and that his store would face west (toward his clientele) with its own entrance.
A dream team
To design the mall, Nasher assembled what amounted to a dream team of consultants who gathered at regular planning sessions in a basement meeting room of downtown’s Southland Center. As lead architect, he selected Harwood K. Smith, whose firm HKS would grow into a Dallas colossus. Landscape was to be a critical component of the design, and to oversee it Nasher engaged an emerging star in San Francisco-based Lawrence Halprin. Graphic designer Herb Rosenthal, from Los Angeles, created the center’s iconic logo, combining a tree and a north-pointing arrow, a visual interpretation of the NorthPark name. (It also resembles the highway cloverleaf adjacent to the mall.)
Also part of the team were the architects brought in to design the anchor stores for Neiman Marcus and Titche-Goettinger. Wanting something that would be both dramatic and modern, Marcus had turned to Eero Saarinen, who had already cemented a place as a leading voice in the architecture profession. He died unexpectedly just as the project was beginning, but Marcus stayed with his Michigan-based firm, under the direction of Kevin Roche and John Dinkeloo.
Lee Star, the director of Titche’s, also wanted something distinctive, and commissioned E.G. Hamilton, a severe Dallasite whose young firm, Harrell & Hamilton, was familiar to Nasher, as it had recently completed his residential tower in Tulsa. There was an added benefit: Hamilton began his career in the office of the modernist Minoru Yamasaki, in suburban Detroit. There he became close friends with a pair of fellow young architects in the area’s close-knit architecture community: Roche and Dinkeloo. Indeed, Dinkeloo was his next door neighbor for more than two years.
Exactly what transpired in those meetings is unclear, but the result was that Hamilton replaced Smith as the lead architect on the project. A significant factor, undoubtedly, was Nasher’s fear that too many architects would create visual chaos. In Hamilton and the team from Saarinen, he knew he had architects with a shared vision and architectural language. “We had two architectural firms who were of like mind,” Hamilton recalled in 2015. “[Roche and Dinkeloo] agreed immediately that we should try to beautify the center. The best way to do this was to do it by a single palette of materials.”
The primary material they chose was brick, but there was some debate over the color. Hamilton wanted gray. Halprin argued for red. They settled on white with a silicone finish, made specially for NorthPark by Henderson Clay Products in Henderson, Texas, a choice that had the advantage of being both aesthetically pleasing and inexpensive.
Settled isn’t quite accurate. The decision was made by Patsy Nasher, an increasing force in the mall’s design development, both out of her own interest and because her husband had a tendency toward indecision. Nasher’s success in business was predicated on painstaking research and analysis, but the flip side of that approach was a certain paralysis when it came time to take action. “If it was left up to Ray and his natural tendencies, we never would have gotten it done,” said Hamilton, of the mall design. Patsy, however, was not one to dawdle. “When Ray would have a hard time making up his mind, I would go see her and she’d help me make up his mind.”
The white brick was offset by dark gray polished concrete floors, another concession to cost. “When Ray first saw it, he thought it was terrible,” Hamilton recalled. But the simplicity of those materials was in fact a virtue, both in their own right and because they augmented the most distinctive and ephemeral element of the design: the natural light that filtered down through skylights and clerestory windows, illuminating broad, uncluttered passages.
Those paths had an unlikely inspiration: New York’s Metropolitan Museum of Art. Hamilton visited the museum during an impasse in the design process, the team having made revision after revision to the plan without a satisfactory solution. The museum’s galleries, with their shifting scales and open courts, suggested an appealing alternative to the long, undifferentiated corridors that defined so many malls. “Although people don’t realize it, they sense the scale that this creates,” Hamilton said.
That strategy also took advantage of one of the site’s challenges, its gradually shifting grade level, and played to the strengths of Halprin, whose work was defined by stepped planes. To manage the transitions in elevation, Hamilton and Richard Vignolo, the Halprin associate who managed the project, created a series of plazas with shifting elevations marked by distinctive fountains.
From the outset, a landscaping program that would bring a sense of the outdoors into the enclosed space was considered essential. Vignolo, working with Patsy Nasher and local landscape designer Richard Myrick, created a vibrant, colorful setting, what he described as a “series of flower shows” running through the center’s passages. Vignolo also created the concrete flower beds and large urns that define the spaces, giving them a sense of orderly calm. Outside, the center was ringed by a 10-acre belt of greenery that softened the approach and marked points of entry.
Architecturally, the most interesting exterior elements were the exposed half-cylinders projecting from the flanks of the Neiman Marcus store. These curiosities, designed by Roche, were the women’s dressing rooms. According to architectural historian Alexandra Lange, author of , a , they were created as something of a sly advertisement, a “minimalist expression of the department store’s most intimate purpose: dressing you.”
The art program for which NorthPark is now famous was in fact a later development. At the time the project began, the only serious work the Nashers owned was a Ben Shahn painting of a tennis player. (Raymond Nasher competed for Duke as an undergraduate.) NorthPark’s first commissioned artwork was a product of the center’s architectural excellence. The Nashers put the proceeds from an early design award toward a site specific work, Dallas Canal, by the sculptor , who lived in their home for some two years during its installation. The piece, composed of Cor-ten steel forms punching out of a 265-foot grass runway, brought a dignified force to the center’s entry from Northwest Highway.
More art came later, after the couple, driven by Patsy, became serious collectors of sculpture. They focused on large-scale works because they were less expensive and easier to acquire. NorthPark became a logical “storage” space where they could rotate their collection. In 2003, they opened the Nasher Sculpture Center in the Arts District as a permanent museum for the bulk of their holdings.
A beautiful morning
A crowd of 55,000 turned out for NorthPark’s opening day, on August 19, 1965. Gordon MacRae, star of stage and screen, led the assembled in a rendition of “Oh, What a Beautiful Morning,” the Rabbi Levi Olan, of Temple Emanu-El, offered a prayer, and then came the cutting of a giant green ribbon that circled the entire complex. And then the stores opened, more than 80 of them, including Neiman’s, Penney’s, Titche’s, Woolworth’s, a Doubleday bookstore, a Kroger supermarket, a Super-X drugstore, eight restaurants, a private club, two theaters and NorthPark National Bank.
NorthPark was hardly the only force that contributed to the gradual decline of downtown Dallas in the years after its opening, but it undoubtedly contributed to it, pulling shoppers off the city streets and into its artfully maintained spaces. Even today, if you’re searching for pedestrians in Dallas, the best place to find them is at NorthPark.
The mall’s success prompted a series of expansions, the first coming in 1972, with the additions of a new wing anchored by Lord & Taylor and a stand-alone bank building. Roughly a decade later, another major expansion pushed the center to over 2 million square feet. But the largest and most significant expansion came in 2006, about a decade after Nancy Nasher, daughter of Raymond and Patsy, gained control of the mall with her husband, David Haemisegger. This transformation took the center’s dogleg plan and squared it off, adding another million square feet of space. The enclosing wing brought a second level traversed by regularly spaced sky bridges, a glassy food court and a multiplex cinema. The hole of this architectural donut became a landscaped open space — CenterPark — suitable for public events.
The expansion was designed by Omniplan, the successor firm of Harrell & Hamilton, and is so respectful of the original as to be essentially seamless. “We decided that we would not touch the existing mall because it was so iconic,” Nancy Nasher said of the new building. A single bay remains of the 1972 expansion (it is directly north of the Neiman’s store). That sense of architectural integrity was achieved by maintaining the material palette — white brick, polished concrete floors — along with the essential design principles of the 1964 structure. “The way light is introduced into the space is very similar to the original, even though it’s a different scale,” said Mark Dilworth in 2015, who took over from Hamilton as the mall’s lead designer at Omniplan. “Like the original, each of the courts is different: different in scale, different in composition. Some are symmetrical, some are asymmetrical.”
The essential character of the space is both strong and restrained enough to accommodate a broad range of retailers, from the highest-end (Neiman’s, Tiffany’s, Gucci) to the more accessible (Macy’s, Zara, Lids), making NorthPark a truly democratic (if consumerist) space. In this it stands in sharp contrast to Highland Park Village, which has been remade from a neighborhood shopping center into an exclusive destination for luxury retail. The clientele at NorthPark, diverse in every way, is a reflection of the city itself. “I believe in its role and its purpose in our city,” says Nasher. “I’m very proud of it.”
A new kind of mall
NorthPark has proven itself a tough act to follow, but that hasn’t stopped developers from trying. The most original attempt was the , five timber-framed levels of quirky craft shops beneath a sky-lit ceiling. It opened in 1973, with a design by Pratt, Box and Henderson, the inventive Dallas architects whose work included the 1964 Apparel Mart, a garment industry trade center with a landscaped plaza of curving forms ringed by open arcades, and the Quadrangle, of 1966, the beloved Uptown shopping center modeled on the urban scale of Santa Fe. All three are now gone.
The most serious competitor to NorthPark is the Galleria, which opened in 1983, offering a new dimension, almost literally, in the mall experience. The massive mixed-use development tacked office towers and a hotel onto a mall hub. The developer, Gerald Hines, had already proven this concept in sprawling Houston, where an earlier Galleria had opened to enormous success.
Both the Houston and Dallas Gallerias were designed by architect , a founding partner of St. Louis-based giant HOK. Like Hamilton, Obata began his career in the office of Minoru Yamasaki, and was similarly inclined to a restrained modernism of raw materiality. (DFW International Airport is another of his Dallas-area projects.) The Galleria’s namesake and inspiration was the Galleria Vittorio Emanuele II, in Milan, an 1861 masterpiece of glass-roofed arcades that converge at a giant glass dome. Obata borrowed those arcades, reinventing them as glazed barrel vaults over a multistory, enclosed environment. The centerpiece was an ice-skating rink. It suggested a new direction for the mall not just as a retail environment but as a total entertainment destination.
Attracting visitors, however, has become an increasing problem for malls. Buffeted by the rise of online shopping, the pandemic and other economic forces, dozens of malls have shuttered, among them Valley View Center, which opened in 1973 and has been largely demolished. That attrition has prompted a healthy rethinking of what the mall can be. Parking lots can be transformed into housing. Mall spaces, bereft of retail, can be reimagined as home to libraries, government services, health care and various other uses, introducing a welcome density into suburban spaces that are trying to reinvent themselves as mixed-use, diverse communities.
Red Bird Mall, which opened in 1975, exemplifies this remaking. Long a problem child, it is now in the midst of a with apartments, health care facilities, office space and — yes — retail. Less successful, , have been the plans to remake Valley View as a multibillion dollar mixed-use development. Originally dubbed “Midtown” and lately the “International District,” plans for it have faltered due to the site’s complicated ownership structure and overly grand ambitions. (No, the development does not need its own cable car system.)
NorthPark, for its part, has managed the mallpocalypse with relative ease, pulling in some 26 million visitors annually. “It’s ever evolving and growing and changing,“ Nancy Nasher says. That mindful attention has assured its status as an international benchmark for retail development, and a genuine civic institution for Dallas.
See you there.
About the Author
Mark Lamster is the architecture critic of the Dallas Morning News, a professor in the architecture school at the University of Texas at Arlington, and a Loeb Fellow at the Harvard Graduate School of Design. His biography of the late architect Philip Johnson, The Man in the Glass House (Little Brown), was a finalist for the 2018 National Book Critics Circle Award for Biography. In 2021, he was awarded the $50,000 Rabkin Prize for arts journalism. Lamster has been a contributing editor to Architectural Review, Design Observer, and ID and writes often for Architect, Architectural Record, and Metropolis, among other design titles. His work has appeared frequently in national publications and magazines, including the New York Times, the Los Angeles Times, and the Wall Street Journal. He is currently working on a new book, a cultural history of Dallas as told through its architecture. It will be published by the Dallas-based non-profit Deep Vellum, and is being serialized in the Dallas Morning News. More about Mark .